Research Summary
Biosensors
In general, lab focusses on developing high-performance, affordable, and easy-to-use diagnostic and monitoring system such as miniaturized sensors for:
- Healthcare (metabolites, biomarkers, tissue, cell, pathogens, etc.)
- Environment (pollutants, chemical residues, pharmaceutical residues, etc.)
- Food & Agriculture (adulterants, chemical residues, etc.)
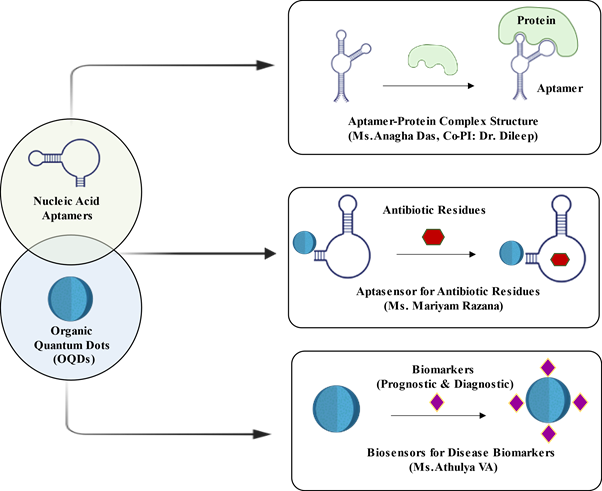
Currently, we are working on developing biosensors for metabolic syndrome (uric acid, lactic acid, adiponectin/leptin) and antibiotic residues from environmental samples. We design and synthesize nucleic acid aptamers (NAAs) and organic quantum dots (OQDs), and investigate the biological and physicochemical properties of synthesized NAAs and OQDs by tuning the precursors or by engineering the surface biochemical properties. We also employed dual detection techniques, i.e., optical and electrochemical.
Another interesting aspect of our study is to look into the aptamer-protein complex interaction using crystal structure analysis to develop better diagnostics and therapeutics.
Publication
- Das, A., Prasad, A., Grewal, A., et al. Fluorescence-based Detection of Uric Acid and Iron using Novel Carbon Nanodots. IEEE Xplore, 2023, 1-6 (DOI: 10.1109/ICST59744.2023.10460777)
Nanomedicine
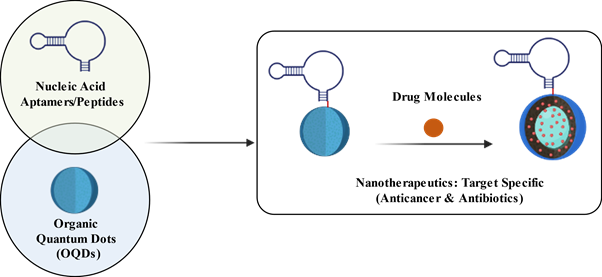
In the lab, we focus on integrating nanotechnology and biomaterials to develop new nanotherapeutics with higher efficiency such as improving biodistribution, controlling delivery of drug molecules, targeting to cells, reduced systemic toxicity and overall improving the drug's efficacy. We work on creating the next generation of smart carriers that are responsive to external triggers and capable of targeting specific cells, with intracellular delivery.
Recently, we worked on different strategies to increase the loading efficiency of drug molecules (Doxorubicin) with carbon nanosphere (pH responsive nanomaterials) for cancer therapeutic (brain cancer).
Publication
- Prasad, A., Sekar, RP., CA Razana, M., et al. High loading and sustained-release system of doxorubicin-carbon dots as nanocarriers for cancer therapeutics. Biomedical Materials, 2024, 19, 065018 (DOI:10.1088/1748-605X/ad7f3a).
Microfluidic Systems
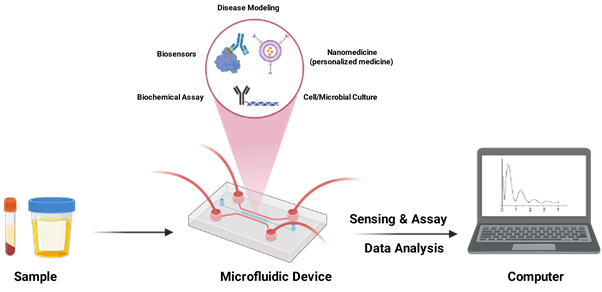
Another interesting vertical of the lab is the integration of microfluidic system by focusing on different aspect of micro- and nano-fluidic by microscopic flow visualization, and microscale impedance spectroscopy.
We study the microfluidic and nanofluidic transport phenomena (on electrokinetic, self-assembly and interface science) and the design of fluidic devices (3D system: lab-on-chip, organ-on-chip, etc. and 2D system: paper-based microfluidics, etc.) with applications in biology, clinical medicine, and biochemical analysis.
Current Research Grants
-
2022 2021
BIG NER Special Call 2020
Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council [BIRAC], DBT, India -
2025 2022
Studies of Non-enzymatic paper-based bioanalytical devices for point-of-care diagnostic applications.
SERB, Department of Science & Technology [DST]