Research Summary
Processing of mRNA UTR and non-coding RNAs: Specificity and cellular implications in diseases All eukaryotic mRNAs (except those encoding histones) harbor poly(A) tail at the 3'-end which is required for stability and efficient translation of the mRNA. There are two major poly (A) polymerases (PAPs) in the nucleus involved in general mRNA polyadenylation - canonical PAPα/γ and Star-PAP. While only one third of human mRNAs are polyadenylated by Star-PAP, majority of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are processed by Star-PAP. Moreover, at the 3’-end of mRNAs,polyadenylation occurs alternately at multiple sites in more than 70% of human genes(APA), encoding mRNA isoforms with different lengths that modulates gene expression. We are interested in understanding the mechanism of PAP specificity, regulation of alternative polyadenylation, processing of ncRNAs and mRNAs, and cellular implications in cardiovascular disease (CVD), cancer, and diabetes. We focus on the non-canonical PAP, Star-PAP that targets mRNA selectively for polyadenylation. We demonstrated a mechanism of PAP specificity, where Star-PAP recognizes a distinct element and excludes PAPα from the 3'-UTR. Various signalling pathways influencethis specificity through phosphorylation(s) of Star-PAP and association with unique co-regulators. We identified unique Star-PAP associated factor- RNA binding motif 10 (RBM10) as a regulator of cardiac hypertrophy (CH)and heart failure (HF) and phosphoinositide synthesizing enzyme PIPKIα in cancer metastasis.In both cellular and animal models for CH, RBM10and Star-PAP expression is down regulated resulting in reduced expression of anti-hypertrophic genes. In addition, Star-PAP-mediated 3'-end processing acts as a key anti-invasive mechanism in cancer cells that requires the co-regulator PIPKIα. Star-PAP knockdown increases cellular invasiveness in breast carcinoma. These functions are regulated through phosphorylation(s) downstream of signalling pathways, and we identified ~20 such variable phosphorylation events on Star-PAP.Investigation of thesesignalling pathways and the consequencephosphorylation events will be crucialto understand how Star-PAP regulates cellular functions and outcomes in CVDs and cancer.
Research Programs
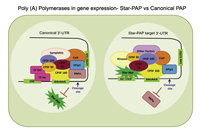
Eukaryotic mRNAs are processed at the 3'-end in a two-step event: an endonucleolytic cleavage followed by addition of an adenosine tail by poly(A) polymerases (PAPs). Star-PAP and PAPa/? are the two primary PAPs in the nucleus involved in nuclear polyadenylation of mRNAs. While the two PAPs share similar processing factors, they regulate distinct niche of target mRNAs. Moreover, polyadenylation occurs alternately at multiple sites at the 3'-end in more than 70% of human genes (APA), encoding mRNA isoforms with different lengths that modulates gene expression. We are interested in defining the mechanism how different PAPs select target mRNAs and how these targets are exclusive for each PAP. We also study regulation of PAP specificity by post-translational modification, and how UTR specificity regulates alternative polyadenylation. 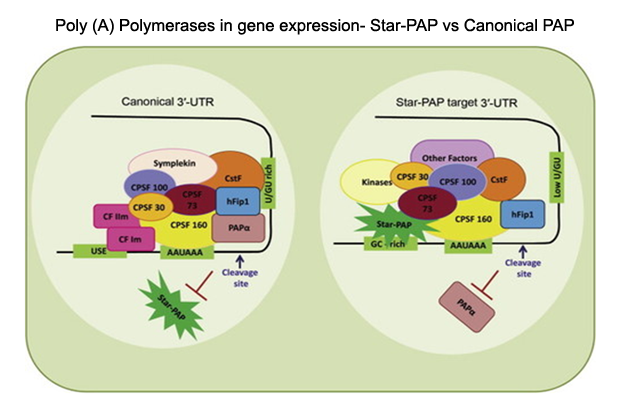
RNA binding motif protein 10 (RBM10) is a regulator of alternative splicing of apoptotic genes. We have identified a splicing independent function of RBM10 that regulates mRNA 3'-end processing of cardiac genes in hypertrophy in the heart and heart failure. We are interested in how RBM10 regulates cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure and signaling pathways involved in the regulation. We also study post-translational modifications such as phosphorylation in RBM10 in the regulation of cardiac gene expression in heart failure.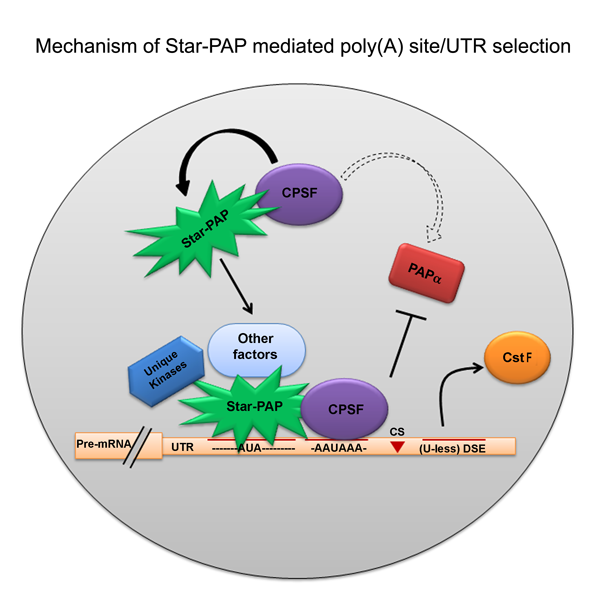

We have reported that majority of long non-coding RNAs (LncRNAs) are processed or regulated by Star-PAP. While most LncRNAs are polyadenylated, some have modified 3'-end. Interestingly, majority of the mRNAs/lncRNAs targeted by Star-PAP are involved cancer metastasis (CM) and metabolic diseases such as diabetes (DM). Preliminary observation suggest different processing pattern between mRNAs and lncRNAs under different disease conditions. Moreover differential Star-PAP level has been reported in CM and DM. We are interested to understand the difference in the mechanism of mRNA and lncRNA processing and how they are affected by signalling pathways under different diseases conditions.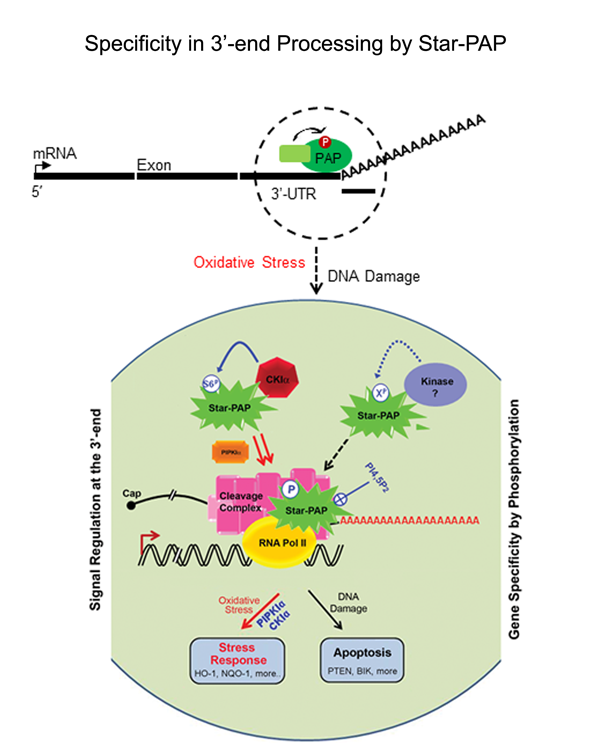
Poly(A) tails are present not only on eukaryotic mRNA 3'-end but also on some of the bacterial mRNAs. While polyadenylation stabilizes mRNA in eukaryotes, presence of poly(A) tail marks degradation of bacterial mRNA. However, the exact mechanism for the functional difference is not known. Here, we aim to define the basic mechanism of mRNA stability between the two organisms and determine what links the two polyadenylation and stabilization pathways. Our transcriptomics data strongly suggests putative role of polyadenylation dependent mRNA stabilization in stress response, bacterial pathogenesis and nutrient starvation. 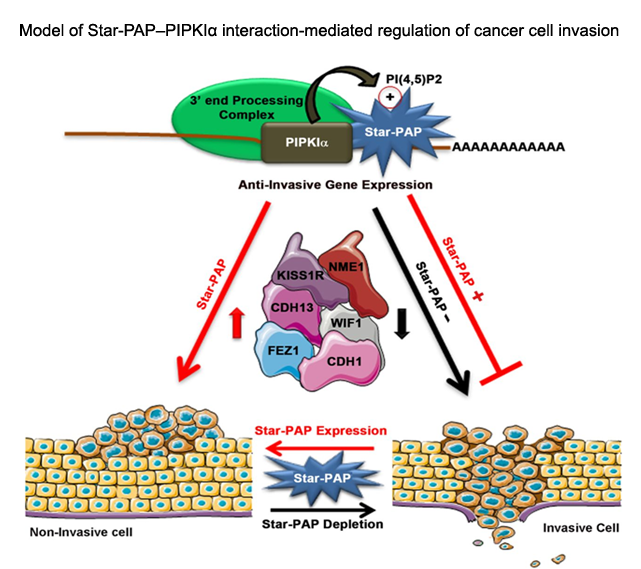

Lipotoxicity is a metabolic disorder that results from the over-activation of lipid signalling pathways leading to the accumulation of lipid intermediates in cells causing cellular distress and ultimately leads to Lipoapoptosis. Heart is one of majorly affected organ as it has a high caloric need for its functioning and performs extensive oxidation of fatty acids (FAs) to meet its requirements. Any disturbance in this fine-regulated network will lead to cardiac lipotoxicity resulting in cardiac dysfunction and heart failure. Preliminary studies in the laboratory have shown that most of the genes and lncRNAs involved in lipid metabolism are modulated by the 3?-end mRNA processing mediated through the Phosphoinositide (PI) signalling. We aim to understand the post-transcriptional regulation of lipid metabolizing genes affecting the lipid composition and the impact on PI signalling during the lipotoxic stress.
Current Research Grants
-
2025 2020
Alternative polyadenylation in gene expression implications in cardiovascular diseases
Swarna Jayanthi Fellowship, Department of Science and Technology, Govt. of India [DST/SJF/LS/2019/145] -
2023 2020
Star PAP control of 3' end processing and alternative polyadenylation in cancer progression
SERB, Science and Technology, [Govt. of India CRG/2019/003230]
Previous/ Completed Research Grants
-
-
3'UTR Regulation of cardiac genes with roles in pressure overload cardiac hypertrophy.
Department of Biotechnology, Govt. of India- 2017 [BT/PR13008/MED/30/1497/2015] 2017-2020 -
Linking the poly (A)tails -Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes
Department of Biotechnology, Govt. of India [BT/PR13008/BAS/30/2015]- 2016 2016-2020 -
Splicing independent function of RNA binding protein RBM 10 in gene regulation and 3'-end processing
SERB, Science and Technology, Govt. of India [EMR/2015/000747]- 2017 2017-2020 -
Specificity and mechanism of Star PAP mediated alternative polyadenylation 3'- end processing in gene expression.
Wellcome Trust-DBT India Alliance Grant [IA/I/12/1/500508]- 2012 2012-2017 -
Regulation of 3'- end processing in oxidative stress response -role of poly (A) polymerases
IYBA, Department of Biotechnology, Govt. of India 2013-2016
-